Introduction
Until this moment I've used the AdventureWorks database (delivered with SQL Server) for building SQL cases, testing some SQL code, proof of concepts, etc. Now, I'm currently working at a client who have millions of records in certain tables. I couldn't find a large table in the AdventureWorks database that contains millions of records. Initially, I was building some ETL scripts on small tables. These ETL scripts are being developed for loading SCD II dimensions. As said earlier, the client has huge tables, that would and should be modelled as dimensions. The Adventureworks database is a great database but I wanted a database that would represent my current client situation in a better way. I've asked Thomas Kejser if he knows a database example that could be used for my problem and he came up with the TPC-H database example. My friend Google, helped me finding more information about the TPC benchmarks. There a couple of bloggers and sites relevant for this post:Take a look at them if you're interested in more information about TPC benchmarks. There are multiple benchmarks available like TPC-C, TPC-E and TPC-Energy.
TPC-H Benchmark
From the TPC website: "The TPC Benchmark™H (TPC-H) is a decision support benchmark. It consists of a suite of business oriented ad-hoc queries and concurrent data modifications. The queries and the data populating the database have been chosen to have broad industry-wide relevance. This benchmark illustrates decision support systems that examine large volumes of data, execute queries with a high degree of complexity, and give answers to critical business questions."The TPC-H Benchmark can be used to examine large volumes of data, execute queries with a high degree of complexity and a supposed answer to critical business questions.
Installation
There seems to be a data file generation tool present on the TPC website. The following installation steps I've taken:1. Download the ZIP file (version 2.14.3) or the tgz file from the Official TPC site. The size of this zip file is about 25,7 MB. I didn't manage to extract the zip file (unrecognized file format (with Windows zipper and Winzip) and therefore I unzipped the .tgz file.
2. The dataset is built using an application in C++. I opened the project files using Visual Studio 2012 Express, built them, and got a resulting dbgen.exe file.
3. In the debug folder the DBGEN.exe tool is present when the build is done.
4. The initial execution of the DBGEN.exe tool generated an error: "Open failed for dists.dss". I found the file (in map above) and copied this to the debug folder. I think that isn't a proper way to do this but it was a quick win;-).
Using the DBGEN tool
I ran the tool DBGEN.exe again and the following files were generated:
- Customer.tbl
- Lineitem.tbl
- Nation.tbl
- Orders.tbl
- Part.tbl
- Partsupp.tbl
- Region.tbl
- Supplier.tbl
On the site of Pilho Kim you'll find CREATE TABLE scripts of MySQL. I've used them as a base for my CREATE TABLE scripts:
USE [TPCD]
GO
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[SUPPLIER]') AND type in (N'U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[SUPPLIER]
GO
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[REGION]') AND type in (N'U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[REGION]
GO
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[PARTSUPP]') AND type in (N'U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[PARTSUPP]
GO
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[PART]') AND type in (N'U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[PART]
GO
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[ORDERS]') AND type in (N'U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[ORDERS]
GO
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[NATION]') AND type in (N'U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[NATION]
GO
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[LINEITEM]') AND type in (N'U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[LINEITEM]
GO
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[CUSTOMER]') AND type in (N'U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[CUSTOMER]
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[CUSTOMER]') AND type in (N'U'))
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[CUSTOMER](
[C_CUSTKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[C_NAME] [varchar](25) NOT NULL,
[C_ADDRESS] [varchar](40) NOT NULL,
[C_NATIONKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[C_PHONE] [char](15) NOT NULL,
[C_ACCTBAL] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[C_MKTSEGMENT] [char](10) NOT NULL,
[C_COMMENT] [varchar](117) NOT NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[LINEITEM]') AND type in (N'U'))
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[LINEITEM](
[L_ORDERKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[L_PARTKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[L_SUPPKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[L_LINENUMBER] [int] NOT NULL,
[L_QUANTITY] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[L_EXTENDEDPRICE] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[L_DISCOUNT] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[L_TAX] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[L_RETURNFLAG] [char](1) NOT NULL,
[L_LINESTATUS] [char](1) NOT NULL,
[L_SHIPDATE] [date] NOT NULL,
[L_COMMITDATE] [date] NOT NULL,
[L_RECEIPTDATE] [date] NOT NULL,
[L_SHIPINSTRUCT] [char](25) NOT NULL,
[L_SHIPMODE] [char](10) NOT NULL,
[L_COMMENT] [varchar](44) NOT NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[NATION]') AND type in (N'U'))
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[NATION](
[N_NATIONKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[N_NAME] [char](25) NOT NULL,
[N_REGIONKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[N_COMMENT] [varchar](152) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[ORDERS]') AND type in (N'U'))
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[ORDERS](
[O_ORDERKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[O_CUSTKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[O_ORDERSTATUS] [char](1) NOT NULL,
[O_TOTALPRICE] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[O_ORDERDATE] [date] NOT NULL,
[O_ORDERPRIORITY] [char](15) NOT NULL,
[O_CLERK] [char](15) NOT NULL,
[O_SHIPPRIORITY] [int] NOT NULL,
[O_COMMENT] [varchar](79) NOT NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[PART]') AND type in (N'U'))
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[PART](
[P_PARTKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[P_NAME] [varchar](55) NOT NULL,
[P_MFGR] [char](25) NOT NULL,
[P_BRAND] [char](10) NOT NULL,
[P_TYPE] [varchar](25) NOT NULL,
[P_SIZE] [int] NOT NULL,
[P_CONTAINER] [char](10) NOT NULL,
[P_RETAILPRICE] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[P_COMMENT] [varchar](23) NOT NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[PARTSUPP]') AND type in (N'U'))
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[PARTSUPP](
[PS_PARTKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[PS_SUPPKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[PS_AVAILQTY] [int] NOT NULL,
[PS_SUPPLYCOST] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[PS_COMMENT] [varchar](199) NOT NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[REGION]') AND type in (N'U'))
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[REGION](
[R_REGIONKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[R_NAME] [char](25) NOT NULL,
[R_COMMENT] [varchar](152) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[SUPPLIER]') AND type in (N'U'))
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[SUPPLIER](
[S_SUPPKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[S_NAME] [char](25) NOT NULL,
[S_ADDRESS] [varchar](40) NOT NULL,
[S_NATIONKEY] [int] NOT NULL,
[S_PHONE] [char](15) NOT NULL,
[S_ACCTBAL] [decimal](15, 2) NOT NULL,
[S_COMMENT] [varchar](101) NOT NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
END
GO
And now the part that took quite some time to get this thing working: importing the files with bcp into the SQL Server tables. Every option I tried gave me the following error and it was driving me nuts.
> bcp TPCD.dbo.SUPPLIER in supplier.tbl -w -t"|" -T
Starting copy...
SQLState = S1000, NativeError = 0
Error = [Microsoft][SQL Server Native Client 11.0]Unexpected EOF encountered in
BCP data-file
0 rows copied.
Network packet size (bytes): 4096
Clock Time (ms.) Total : 16
I found a blogpost on the Shades of orange site and a suggestion was/is done, that the problem could be in the encoding of the file. I changed the coding from ANSI to UCS-2 Little Endian in Notepad++ and it worked just fine.
This seems to be the problem and now the file is properly imported into the SUPPLIER table.
>bcp TPCD.dbo.SUPPLIER in supplier.tbl -w -t"|" -T
Starting copy...
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 1000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 2000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 3000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 4000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 5000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 6000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 7000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 8000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 9000
1000 rows sent to SQL Server. Total sent: 10000
10000 rows copied.
Network packet size (bytes): 4096
Clock Time (ms.) Total : 531 Average : (18832.39 rows per sec.)
All files are imported into SQL Server, except one and that is the LineItem files. I've used the following command lines and I've converted all files to UCS-2, except the LineItem file. That file gave some troubles.
bcp TPCD.dbo.SUPPLIER in supplier.tbl -w -t"|" -T
bcp TPCD.dbo.REGION in REGION.tbl -w -t"|" -T
bcp TPCD.dbo.PART in PART.tbl -w -t"|" -T
bcp TPCD.dbo.NATION in NATION.tbl -w -t"|" -T
bcp TPCD.dbo.PARTSUPP in PARTSUPP.tbl -w -t"|" -T
bcp TPCD.dbo.CUSTOMER in CUSTOMER.tbl -w -t"|" -T
bcp TPCD.dbo.ORDERS in ORDERS.tbl -w -t"|" -T
bcp TPCD.dbo.LINEITEM in LINEITEM.tbl -w -t"|" -T
The size of the LineItem file is about 750 MB and my Laptop and/or notepad++ doesn't seem to handle this huge text file. I'm recieving the following error: "File is too big to be opened by Notepad++"....This is bad! Now I have to find another tool to convert the file (for only the last one grmph)..After trying some options I found the tool "Text File Splitter 2.0.4". I downloaded it and used the tool for splitting the LINEITEM file into smaller chunks of 1 million rows. Then, I opened the chunk files into notepad++, converted it to the UCS-2 and imported it with BCP. Finally, it worked.
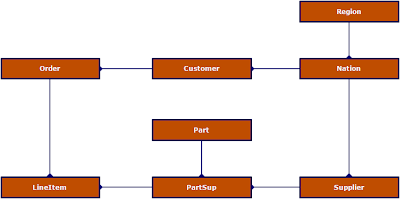
The TPC-H 3NF datamodel
The datamodel that I have created from analyzing the physical tables is shown below. This a typical order entry system that has two transaction tables (Order and LineItem) and multiple Master data tables Region, Nation, Customer, Supplier and PartSup. PartSup is n:m table between Supplier and Part, probably because a supplier can deliver multiple parts and a part can be delivered by multiple suppliers.The TPC-H dimensional datamodel
This paragraph explains a possible design of a dimensional datamodel. The dimensional datamodel itself is a derivative of the TPC-H datamodel where the structure of the database has been transformed into a star schema, also dropping columns. The dimensional datamodel aligns with the advise and practices considered optimal by Kimball.There are two Star Schema Benchmark papers that I have been able to access & use. The 2007 paper here, and the 2009 revision (the 3rd revision apparently) of this paper here.
Conclusion
The TPC-H Benchmark is useful addition to the toolset I'm using during developments of SCD dimensions or Datavault implementations.
Greetz,
Hennie